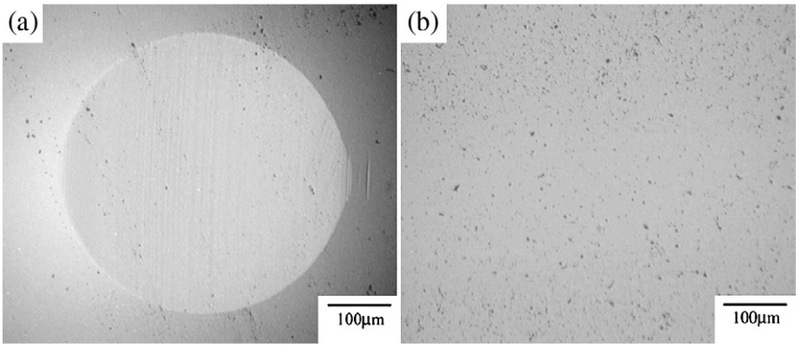
Abstract:Amorphous carbon nitride (a–CNx) coatings were deposited on Si3N4 disks by an ion beam assisted deposition system. The composition, structure and hardness of the a–CNx coatings were characterized by Auger electronic spectroscopy, Raman spectroscopy and nano-indentation tester, respectively. The influences of normal load and sliding speed on the friction coefficients and the specific wear rates for the a–CNx/Si3N4 tribo-pairs were investigated and analyzed synthetically by ball-on-disk tribometer. The worn surfaces were observed by optical microscope. The results showed that the a–CNx coatings contained 12 at.% nitrogen, and their structure was a mixture of sp2and sp3 bonds. The a–CNx coatings’ nanohardness was 29 GPa. The influence of sliding speed on the friction coefficients and the specific wear rate of the CNx coatings was more obvious than that of normal load. The friction coefficients and the specific wear rate of the CNx coatings decreased as the sliding speed increased. At a sliding speed higher than 0.1 m/s, the friction coefficients were less than 0.04. The specific wear rates of the a–CNx coatings were higher than those of Si3N4 balls at a sliding speed below 0.1 m/s, while the specific wear rates of the a–CNx coatings and the Si3N4 balls all fluctuated around a lower level of 10− 8 mm3/Nm as the sliding speed increased beyond 0.2 m/s. To describe the wear behavior of a–CNx coatings sliding against Si3N4 balls in water with normal loads of 3–15 N and sliding speeds of 0.05–0.5 m/s, the wear-mechanism map for the a–CNx/Si3N4 tribo-pairs in water was developed.
全文下载: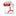 Influence of normal load and sliding speed on the tribological property of amorphous carbon nitride coatings sliding against Si3N4 balls in water.pdf
Influence of normal load and sliding speed on the tribological property of amorphous carbon nitride coatings sliding against Si3N4 balls in water.pdf
