| Controlling direct contact force for wet adhesion with different wedged film stabilities |
| M. Li, J. Xie, L. Shi, W. Huang, X. Wang,J. Phys. D: Appl. Phys,51,165305(7pp),(2018) |
| 发布人:戴庆文 发布时间:2021-01-14 浏览次数:443 |
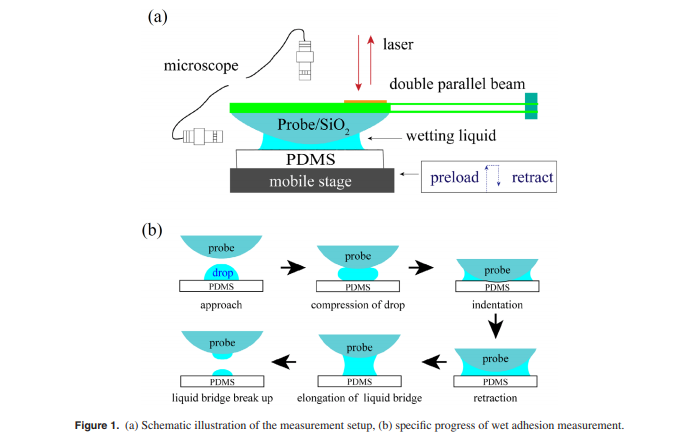
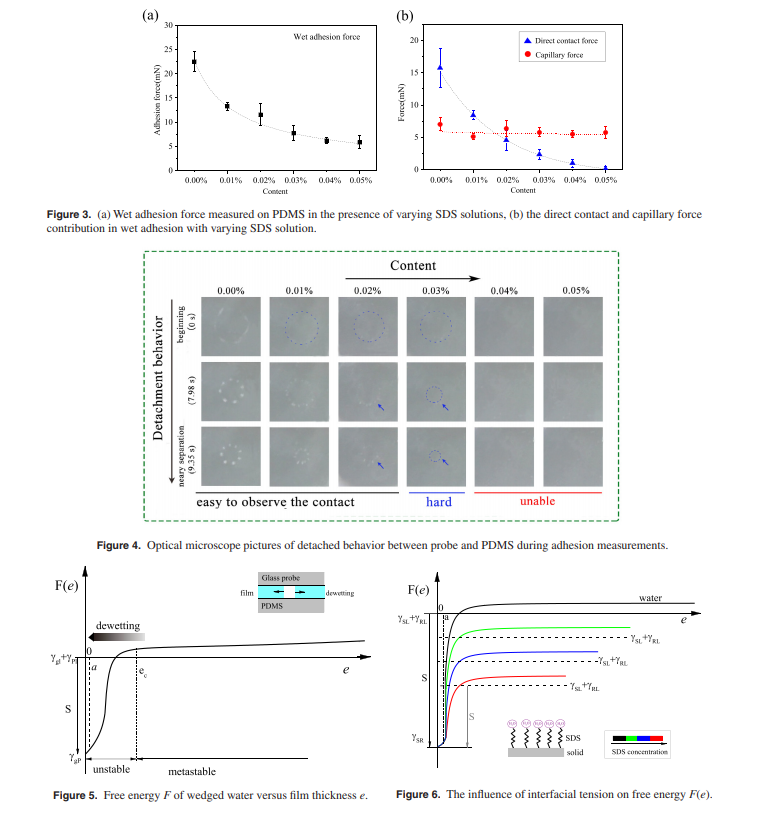
In solid–liquid–solid adhesive systems, wedged films often feature instability at microscopic thicknesses, which can easily disrupt the adhesive strength of their remarkable direct contact force. Here, sodium dodecyl sulfate (SDS) was employed to tune the instability of adhesion in wedged glass–water–rubber films, achieving controllable direct contact. Experimental results showed that the supplement of SDS molecules significantly weakened the direct contact force for wet adhesion and eliminated it at high concentrations. The underlying reason was suggested to be the repulsive double-layer force caused by SDS molecules, which lowers the instability of the wedged film and balances the preload, disrupting the direct contact in wet adhesion. Keywords: sodium dodecyl sulfate, wet adhesion, direct contact force, wedged film, unstability, dewetting.
全文下载: |