| Fretting Characteristics of Textured TC4 Alloy Under Punch/Plane Contact: A Finite Element Study |
| Shenglin Liang, Xuanqi Sun, Dingjun She, Qingwen Dai, Wei Huang, and Xiaolei Wang (2025) |
| 发布人:戴庆文 发布时间:2024-02-23 浏览次数:701 |
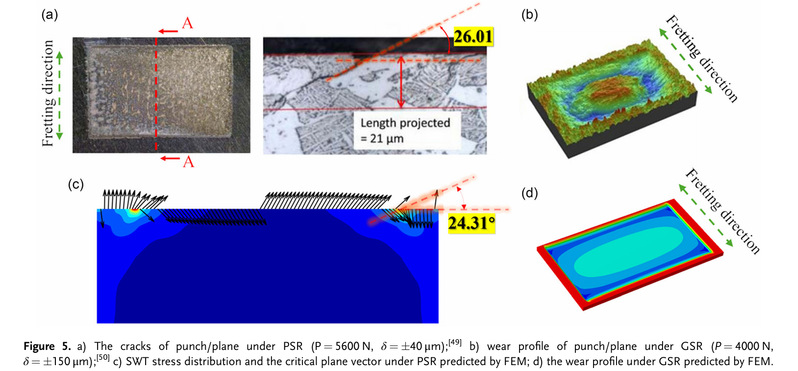
Herein, the fretting behavior of textured surfaces with varying depths under punch/plane conditions for TC4 (Ti-6Al-4 V) is simulated using the finite element method . The effects of surface texture on mechanical properties, wear behavior, and fatigue characteristics are analyzed. The Archard and energy wear models are employed to simulate fretting behavior, while the Smith–Watson–Topper model is utilized to predict the fatigue damage. The interfacial dynamics remained unchanged in the presence of surface textures. Fretting states of the partial slip regime (PSR) or the gross slip regime (GSR) are identical under similar loading conditions for smooth as well as textured surfaces. In the PSR, the primary damage mechanism is fatigue cracking, and the fatigue life of textured surfaces decreased with increasing texture depth. Compared with the smooth sample, the fatigue life of the textured surface with 40 μm groove depth reduces by ≈6.3%. In the GSR, wear is observed to be the dominant damage mechanism, and textured surfaces demonstrated better anti-wear performance at lower displacement amplitudes (≤30 μm) when compared with the smooth surfaces.
全文下载: |