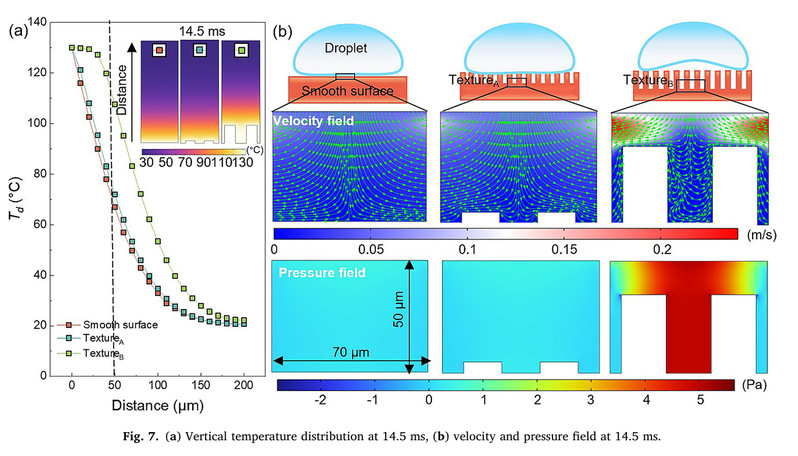
Slippery liquid-infused porous surfaces have broad applications due to their excellent properties, but their performance under high-temperature conditions typical in industry remains underexplored. In this study, textured and slippery surfaces were fabricated via ultraviolet laser processing and chemical modification. The impact behaviors of water, mixture, and emulsion droplets on smooth, textured, and slippery surfaces were examined from 130 °C to 230 °C. Evaporation experiments revealed notably lower static Leidenfrost points for droplets on slippery surfaces—180 °C, 180 °C, and 190 °C for water, mixture, and emulsion, respectively—demonstrating the thermal stability of the slippery surface. Impact mode maps summarized droplet behaviors, and dynamic Leidenfrost points were identified, with water droplets showing values of 160 °C, 160 °C, 190 °C, 130 °C, and 130 °C across five surfaces at impact velocity V=0.9 m/s. Changes in spreading factor and schematics elucidated that co-evaporation of lubricant and water stabilizes the vapor layer and enhances droplet bouncing. Numerical simulations revealed shorter solid–liquid contact times and clarified mechanisms of explosive bounce due to vapor flow variations among surface structures. Thermal resistance and heat transfer models for different surfaces were innovatively developed. These findings fill gaps in prior research lacking thermal considerations and offer theoretical insights for applications in surface self-cleaning, droplet manipulation, and thermal management.
全文下载: Impact behavior of droplets on slippery liquid-infused porous surface under elevated temperatures.pdf
Impact behavior of droplets on slippery liquid-infused porous surface under elevated temperatures.pdf
